Food Adulteration: 7 Shocking Truths You Must Know

Table of Contents
The Hidden Truth Behind Your Everyday Pantry
Food adulteration is no longer a rare scandal, it’s a daily reality silently affecting millions of Indian kitchens.
Every morning, across countless homes, we reach out for our staples: atta, rice, dals, ghee, oils, foods so familiar we rarely pause to question them. They feel safe. They feel trusted. They form the foundation of our meals and our memories.
But what if this trust is misplaced?
Unfortunately, with food adulteration rising across India, that’s exactly what is happening. From chalk-laced flour to artificially polished rice and chemical-dosed spices, adulteration has quietly and dangerously entered everyday life.
This blog uncovers the scale, the science, the health impact, and the solutions every Indian home should know.
1. Healthy or Hacked? Your Pantry Deserves a Closer Look
Food adulteration refers to the deliberate addition, substitution or removal of substances in food, compromising its safety, quality and nutritional value. As per FSSAI, any food altered in a way that lowers its quality or makes it unsafe is considered adulterated.
Despite the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 and the presence of regulatory bodies and state food authorities, adulterated products continue to make their way into kitchens across India. Why?
1) Enforcement gaps: Regular checks, sampling, and prosecution often fall short due to limited manpower and resources.
2) A fragmented food chain: With countless small-scale producers, traders, and middlemen, monitoring every link becomes nearly impossible.
3) Profit over safety: Adulterants like chalk powder in atta or synthetic polish on rice help cut costs, especially when inspections are rare.
4) Low consumer awareness: Most people can’t easily detect adulteration or don’t know how to report it.
So, while your pantry may look safe, what’s inside may not be. The reality is that adulteration isn’t always visible but its impact runs deep.
2. How Deep Does Food Adulteration Really Go?
The truth is unsettling.
Food adulteration in India is not isolated to a few products, it’s a widespread crisis affecting the staples you consume every single day.
Below are real, verified findings:
1) In Rajasthan (2024), 1 in 4 food samples tested were adulterated. Over 6.6 lakh kg of food was seized or destroyed.
2) In 2025, data shared in Parliament revealed over 1,500 of 23,000 spice samples failed safety standards due to non-permitted colors and pesticides.
3) FSSAI’s 2022-23 data showed 18% of pulses tested were substandard or unsafe, frequently containing toxic dyes like metanil yellow.
4) In Delhi and Gujarat (2023), 1 in 4 edible oil samples was adulterated, blended with cheaper oils or contaminated with mineral oil.
5) In Agra, over 25,000 kg of fake ghee was seized made with urea and palm oil, packed to mimic big brands.
Read Our blog to Know More
And this list is only the beginning.
Milk, paneer, fruits, vegetables, honey, coffee, tea, almost every food category has been affected by food adulteration.
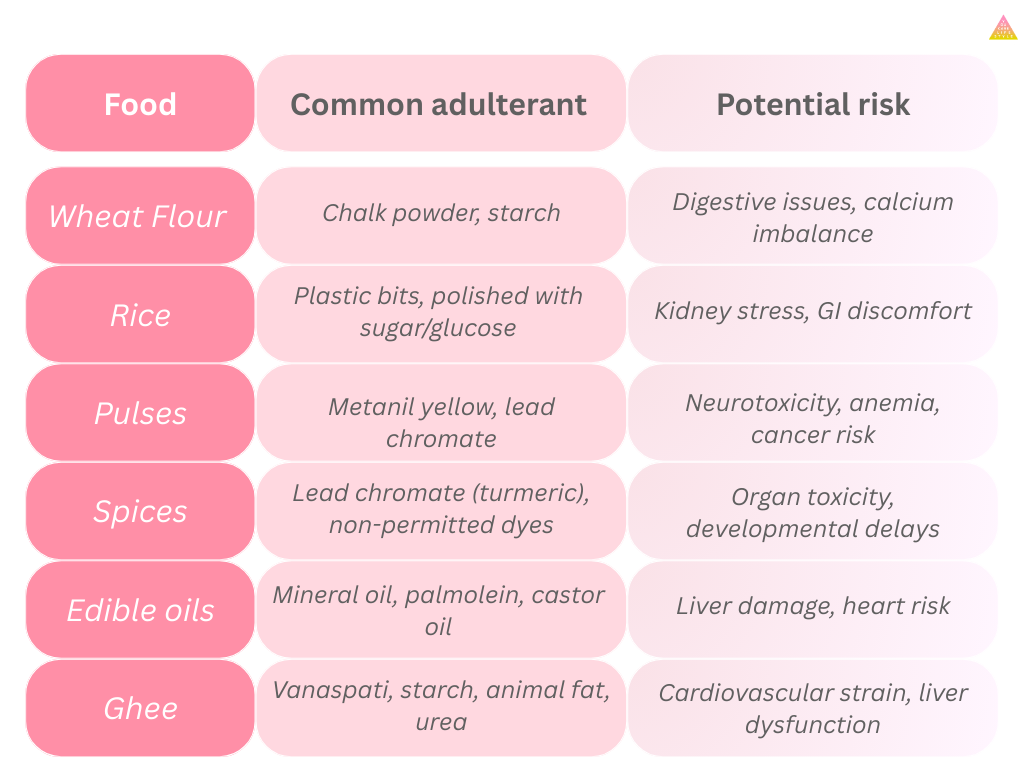
3. Unseen Contaminants Hiding in Your Daily Foods
Take a look at common adulterants in everyday staples and what they can do to your health.
Atta (Flour)
- Common adulterants: Chalk powder, talc
- Risks: Nutrient loss, digestive issues
Rice
- Common adulterants: Synthetic polish, plastic rice (rare but reported)
- Risks: Kidney burden, chemical toxicity
Dals (Pulses)
- Common adulterants: Metanil yellow, textile dyes
- Risks: Carcinogenic potential, organ strain
Milk & Paneer
- Common adulterants: Detergents, starch, urea
- Risks: Gastrointestinal irritation, kidney overload
Edible Oils
- Common adulterants: Mineral oils, cheaper oils
- Risks: Liver damage, long-term inflammation
Spices
- Common adulterants: Sudan dyes, brick powder
- Risks: Severe toxicity, immune suppression
Ghee
- Common adulterants: Vanaspati, palm oil, urea
- Risks: Cardiovascular strain, endocrine disruption
The harsh truth: food adulteration has become deeply embedded in the Indian food ecosystem.
4. What Does Food Adulteration Do to Your Health?
The consequences range from mild to life-threatening:
Short-Term Effects
Digestive issues : Adulterants like chalk powder, starch, detergents, and synthetic dyes can irritate the gastrointestinal tract almost immediately. This often leads to bloating, stomach cramps, acidity, and loose motions, especially after consuming contaminated milk, paneer, or flour.
Skin irritation : Chemical colors and toxins used to enhance the appearance of foods—such as metanil yellow in dals or Sudan dyes in spices, can trigger allergic reactions. Symptoms may include rashes, itching, redness, or flare-ups in individuals with sensitive skin or existing allergies.
Headaches : Artificial additives, low-grade preservatives, and contaminated oils disrupt the body’s natural detox pathways. This can cause mild to severe headaches due to toxin buildup, dehydration, or irritation of the nervous system.
Nausea : Substances like detergent in milk, mineral oil in edible oils, or non-permitted colors can cause an instant feeling of nausea or vomiting. The body reacts this way to expel what it identifies as toxic or foreign.
Long-Term Effects
Liver damage : The liver works overtime to process and neutralize toxic chemicals found in adulterated foods. Over time, exposure to dyes, pesticides, heavy metals, and mineral oils can cause inflammation, fatty liver changes, or severe liver injury.
Kidney failure : Kidneys filter out harmful substances from the blood. Chronic consumption of urea-adulterated ghee, detergent-contaminated milk, or heavy metal–loaded staples puts immense pressure on the kidneys, leading to long-term impairment or even kidney failure in extreme cases.
Hormonal disruption : Certain adulterants, like plasticizers, chemical preservatives, and non-food-grade additives, act as endocrine disruptors. They interfere with hormone balance, affecting metabolism, reproductive health, mood, and overall hormonal function.
Toxic metal accumulation : Foods contaminated with heavy metals like lead, arsenic, mercury, or cadmium accumulate in the body over time. These metals can impair neurological function, weaken bones, reduce immunity, and cause irreversible organ damage.
Increased risk of chronic diseases : Long-term exposure to low-quality oils, synthetic chemicals, and adulterated staples can contribute to the development of diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and inflammatory disorders. The body remains in a constant state of stress due to ongoing toxin exposure.
Possible carcinogenic effects (from dyes & chemical residues) : Certain adulterants such as industrial dyes, chemical colorants, and pesticide residues are classified as potentially carcinogenic. Continuous consumption of such contaminated foods increases the risk of cancers over time, especially those affecting the digestive system and liver.
Children, pregnant women, and the elderly face higher risks due to weaker systems.
5. Decode Before You Bite: Detect Food Adulteration at Home
This is why awareness about food adulteration is not optional, it’s essential.
Being aware is your edge. Acting on it is your power.
While food adulteration in India remains a widespread challenge, action is underway. The FSSAI has ramped up surveillance, seized unsafe products across states and launched consumer-focused campaigns like Eat Right India. State authorities are also conducting surprise raids and tightening penalties.
But real change starts with you.
The FSSAI’s DART Manual (Detect Adulteration with Rapid Test) empowers consumers with simple tests you can perform using basic household items.
Examples
- Turmeric adulteration: Hot water test reveals artificial colors.
- Paneer adulteration: Iodine test reveals added starch.
- Milk adulteration: Soapiness indicates detergent contamination.
- Sugar adulteration: Chalk settles at the bottom when dissolved.
These tests don’t cover every adulterant, but they can detect many common ones.
6. Strengthening Your Rights as a Consumer
The Consumer Protection Act 2019 safeguards you from food fraud and empowers you to take action against brands or sellers who compromise your safety.
Consumers can:
- File complaints online via National Consumer Helpline (NCH 1915)
- Seek compensation for harm
- Report unsafe food via FSSAI’s Food Safety Connect app
Regulators can:
- Investigate
- Prosecute
- Fine violators
- Remove adulterated products from circulation
The more consumers report, the stronger the system becomes.
7. Smart Habits That Protect Your Family
To reduce your exposure to food adulteration, adopt these habits:
Check the Label, Always look for:
- FSSAI license
- Batch and lot number
- Manufacturing date
- Expiry date
- Ingredient list
Buy From Trusted Sources
Choose retailers and brands known for maintaining strict quality control, ethical sourcing, and consistent transparency. Reputable sellers are far less likely to compromise on safety because their credibility depends on it. Whether shopping online or offline, prioritizing trusted sources reduces your risk of bringing home products contaminated with adulterants, hidden fillers, or poor-quality substitutes.
Prefer Third-Party Tested Products
Always look for products that undergo independent, third-party laboratory testing. These tests check for heavy metals, pesticide residues, microbial contamination, and label accuracy. Third-party verification adds an extra layer of accountability because the results come from unbiased labs, not internal claims. Certifications and test reports ensure that what you’re buying meets the safety standards you expect.
Avoid Unusually Cheap Products
If a product is being sold at a price significantly lower than usual market rates, consider it a red flag. Extremely cheap staples like ghee, oils, dals, or spices often indicate the use of inferior ingredients, harmful additives, or substitution with cheaper inputs. Adulteration is most profitable when cutting corners reduces cost. So if the price feels too good to be true, it almost always is.
These habits serve as your first line of defense against food adulteration.
Choose Trust. Choose Pink Tiger
At YouCare Lifestyle, we understand the value of purity in what you consume. That’s why we rigorously vet every product we offer to ensure it meets the highest safety, quality and authenticity standards.
Our verified products undergo a strict selection process, free from artificial additives, chemicals or contaminants. We go beyond just offering healthier alternatives, we’re here to empower you to make informed decisions. Products are rigorously tested for:
1) Heavy metals
2) Pesticides
3) Microbial safety
4) Label accuracy
We handle all the heavy lifting so you can enjoy worry-free, clean and verified products. Because when you choose Pink Tiger, you choose peace of mind.

Final Thought
Food adulteration isn’t just a regulatory challenge, it’s a personal one. It affects the meals we cook, the ingredients we trust, and the health of the people we love most. While the problem may seem widespread and deeply rooted, the solution begins with awareness and intention. Every time you choose a product backed by transparency, every time you read a label instead of assuming safety, and every time you invest in purity over price, you shift the market in the right direction.
Your daily choices have power, far more than manufacturers and sellers expect. When consumers demand honesty, the industry is forced to rise to higher standards. This is how change begins: one conscious purchase, one verified product, one informed household at a time.
Remember, your pantry is more than a shelf of groceries. It’s the foundation of your family’s health, energy, growth, and long-term well-being. So stay curious, stay vigilant, and choose brands that honor your trust instead of exploiting it. Because clean, safe, and authentic food shouldn’t be a privilege it should be the default. And with greater awareness, it can be.
Your kitchen deserves purity. Your family deserves safety. And you deserve peace of mind every single day.
Check out our Instagram for Food Adulteration Posts
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What exactly is food adulteration?
Food adulteration refers to the intentional or accidental contamination, dilution, or alteration of food with substances that reduce its quality, purity, and safety. It includes adding harmful chemicals, substituting ingredients with inferior alternatives, or removing valuable nutrients, often to reduce production costs or increase shelf life.
2. Why is food adulteration so common in India?
Food adulteration thrives due to fragmented supply chains, limited enforcement capacity, low consumer awareness, and high profit margins for producers and middlemen who use cheap additives. With millions of small-scale vendors and inconsistent monitoring, adulterants can easily slip into daily staples without immediate detection.
3. What are the most commonly adulterated foods in India?
Staples such as milk, paneer, rice, dal, ghee, coffee, spices, and edible oils are among the most commonly adulterated products. Common adulterants include starch, detergents, metanil yellow, mineral oils, artificial colors, and cheaper edible oils blended to mimic premium varieties.
4. How can I check for adulteration at home?
Simple home tests described in FSSAI’s DART Manual can detect many adulterants. For example, adding iodine to paneer reveals starch, dissolving sugar reveals chalk, and heating ghee shows whether it contains vanaspati. While not comprehensive, these tests offer a quick first-level screening.
5. How can I avoid adulterated food?
Always buy from trusted brands, check labels carefully, avoid unusually cheap products, look for third-party testing, like the Pink Tiger Verification and choose retailers known for strict quality control. Verified products with transparent testing are the safest way to reduce your exposure.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider before trying any new food items, supplements, or products.
References
1) Choudhary, A., Gupta, N., Hameed, F., & Choton, S. (2020). An overview of food adulteration: Concept, sources, impact, challenges and detection. International Journal of Chemical Studies, 8(1), 2564–2573. https://doi.org/10.22271/chemi.2020.v8.i1am.8655
2) Soopa, M. S., & Panwar, K. S. (2020). Food adulteration in contemporary India: Emerging trends and remedies. SOCRATES, 8(1), 64–71. https://doi.org/10.5958/2347-6869.2020.00008.4
5) Nath, P. P., Sarkar, K., Tarafder, P., Mondal, M., Das, K., & Paul, G. (2015). Practice of using metanil yellow as food colour to process food in unorganized sector of West Bengal – a case study. International Food Research Journal, 22(4), 1424–1428. http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my/22%20(04)%202015/(16).pdf
6) Patil, A. G., Banerjee, S., & Yadav, S. T. (2025). Impact of adulterants on quality of edible oils. Wiley Online Library, 211–242. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781394186426.ch9

