Heavy Metals in Chocolate: 5 Risks Turning into Toxic Treats

From childhood to adulthood, chocolate has been our favourite sweet treat. Whether it’s a simple chocolate bar or a decadent truffle, the rich and indulgent flavour is hard to resist. Its versatility in desserts and confections makes it a beloved ingredient in many cuisines. However, recent findings have detected traces of heavy metals in chocolate. What does this mean for chocolate lovers like us?
Table of Contents
When Your Favourite Treat Gets a Reality Check
Chocolate is more than a dessert. For many, it’s a hug in edible form, a moment of comfort, celebration, or pure indulgence. But as much as chocolate evokes joy, a growing conversation is unfolding around something far less sweet: heavy metals in chocolate.

Recent multi-year analyses, evaluating 72 dark chocolate and cocoa products, highlight a worrying pattern, some chocolates contain measurable levels of lead, cadmium, arsenic, and mercury. While these levels do not make chocolate “dangerous” in normal quantities, the concern is real. Frequent, long-term exposure to these metals can potentially turn your indulgence into a “toxic treat.”
But here’s the good news: you don’t need to give up chocolate. You just need to understand why heavy metals end up in chocolate, how they may affect your health, and what you can do to choose safer, cleaner options.
This blog brings you clear explanations, and practical choices, so you can continue to enjoy chocolate with confidence.
The Wonderful Benefits of Cacao and Dark Chocolate
Before diving into risks, let’s not forget why dark chocolate has earned such a celebrated place in nutrition and wellness. The research is compelling, when sourced and consumed wisely, cacao offers truly powerful benefits.
1. A Potent Antioxidant Powerhouse
Cacao is naturally packed with powerful flavonoids like epicatechin, plant-based antioxidants that work to neutralise harmful free radicals in the body. By reducing oxidative stress, these compounds help lower chronic inflammation, a root cause behind conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and premature ageing. Epicatechin also supports healthier blood vessels, improves cellular repair, and enhances the body’s resilience against everyday environmental and dietary stressors, making cacao one of the most potent antioxidant foods you can enjoy.
How they work:
Neutralise free radicals: These unstable molecules cause oxidative stress, contributing to aging and chronic disease.
Reduce inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a precursor to metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune issues.
Protect cells: Flavonoids support cellular repair and strengthen the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
Research Insight:
A large systematic review concluded that cocoa flavanols significantly improve markers of oxidative balance and vascular health. This positions cacao as one of the most antioxidant-rich foods on the planet.
2. A Heart-Friendly Indulgence
Cacao improves cardiovascular function through several synergistic pathways, primarily by increasing nitric oxide production, enhancing endothelial function, reducing oxidative stress, and supporting healthier blood pressure responses. Flavanols like epicatechin help relax blood vessels, improve blood flow, and reduce inflammation all of which collectively contribute to stronger, more resilient cardiovascular health.
How it helps the heart:
▪️Increases nitric oxide (NO) production, which relaxes blood vessels
▪️Enhances endothelial function, essential for healthy arteries
▪️Improves circulation to major organs
▪️May lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure
Why it matters:
Better circulation means more oxygen and nutrients reach every part of the body, supporting long-term heart health.
3. Boosts Mood & Cognitive Performance
Chocolate’s mood-enhancing effects aren’t just psychological, they’re biochemical. Cacao contains naturally occurring compounds like serotonin precursors, dopamine boosters, and anandamide, famously known as the “bliss molecule,” which directly interact with your brain’s feel-good pathways. These compounds help elevate mood, reduce stress, and promote relaxation by influencing neurotransmitter activity. In addition, cacao flavonoids increase blood flow to the brain, supporting focus, mental clarity, and a sense of calm alertness. So when chocolate lifts your mood, it’s not just comfort it’s chemistry at work.
What cacao activates:
▪️Serotonin: stabilises mood and reduces anxiety
▪️Dopamine: enhances motivation, satisfaction, and pleasure
▪️Anandamide: also called the “bliss molecule”
▪️Phenylethylamine (PEA): associated with excitement and attraction
Cognitive benefits:
▪️Increases blood flow to the brain
▪️Enhances concentration, mental clarity, and memory
▪️Reduces stress-induced cognitive fog
Cacao essentially acts as a natural nootropic.
4. Enhances Athletic Performance
Athletes are turning to cacao not just for its rich flavour but for its scientifically supported performance benefits. Cacao is naturally high in flavanols, which boost nitric oxide production, a compound that widens blood vessels, improves circulation, and enhances oxygen delivery to working muscles. This translates into better endurance, reduced fatigue, and improved recovery after strenuous workouts. Research also shows that cacao’s antioxidants help fight exercise-induced oxidative stress, while its magnesium content supports muscle function, energy production, and cramp prevention. Together, these effects make cacao a powerful, natural addition to pre-workout routines for athletes seeking cleaner, plant-based ways to enhance stamina and speed up recovery.
How it helps:
▪️Boosts oxygen delivery during exercise
▪️Speeds up muscle recovery by reducing oxidative damage
▪️Improves VO2 max, aiding endurance
▪️Enhances blood flow to working muscles
This makes cacao especially popular for pre-workout snacks.
5. Helps Manage Cravings & Satiety
High-quality dark chocolate supports healthier eating patterns by offering slow-release energy, reducing sugar cravings, and promoting satiety, which helps you avoid mindless snacking. Its rich flavonoids stabilize blood sugar levels, curb the urge for overly sweet foods, and encourage more mindful, satisfying indulgence, ultimately helping you build a more balanced and controlled approach to eating.
How:
▪️Contains healthy fats that slow digestion
▪️Smaller portions feel satisfying
▪️Prevents sugar binges
▪️Provides magnesium, which reduces stress-driven cravings
People often find that just one or two squares satisfy the urge for sweets—unlike ultra-processed snacks that trick the brain into overeating.
What are Heavy Metals?
Heavy metals are elements that occur naturally but become harmful when they accumulate in the human body.
The primary heavy metals found in chocolate are:
▪️Lead
▪️Cadmium
▪️Arsenic
▪️Mercury
How They Enter Chocolate
There are two main pathways:
1. Soil Absorption During Cultivation
Cocoa plants are highly absorptive.
They pull minerals including heavy metals from the soil they grow in.
Factors that increase soil metals:
▪️Volcanic soils (high in cadmium)
▪️Industrial pollution
▪️Mining runoff
▪️Pesticide contamination
▪️Poor soil management
Cadmium is the biggest concern here, especially in cocoa grown in South America.
2. Processing & Post-Harvest Contamination
Lead often enters chocolate after harvest.
Sources include:
▪️Open-air fermentation where dust particles settle on beans
▪️Contaminated equipment used for grinding
▪️Storage containers
▪️Shipping materials
▪️Old, rusting factory machinery
Research suggests lead contamination tends to occur later in the supply chain, not on the farm.
What Heavy Metals Mean for Your Health?

You may have heard that tiny amounts of heavy metals like lead, cadmium, mercury, and arsenic can find their way into chocolate. But what does that imply for you? These metals, present in soil and the environment, can cause health problems if they accumulate in your body over time. Here’s a simple breakdown of why these metals are a concern:
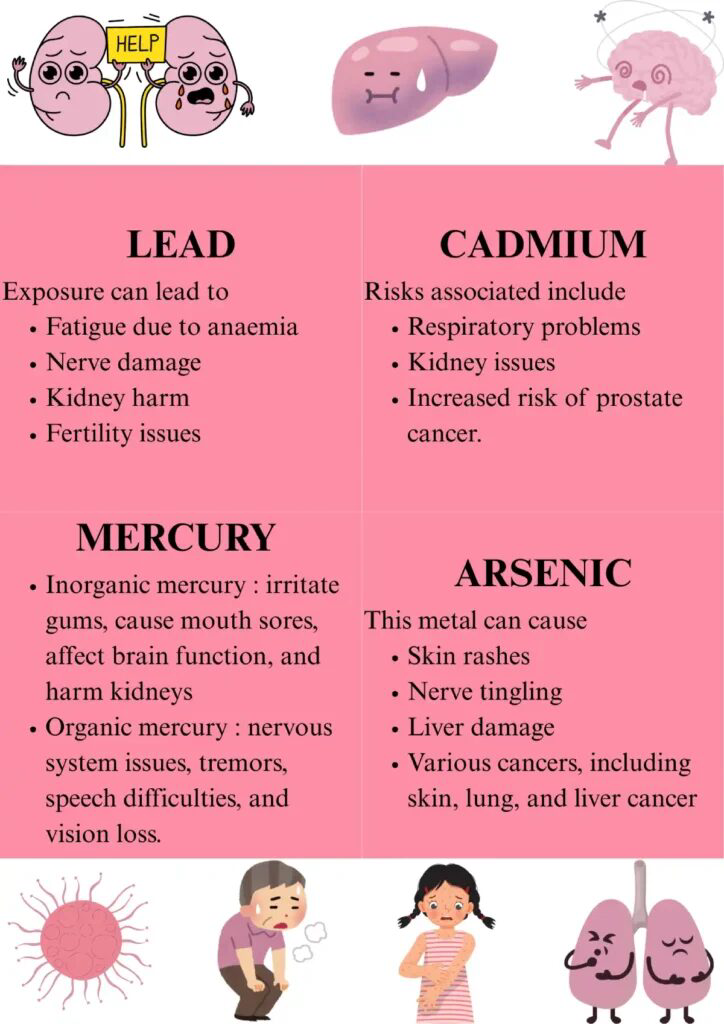
Lead: Impacts the Brain and Nervous System
Lead is particularly harmful because the body struggles to eliminate it.
Potential long-term effects:
▪️Reduced cognitive performance
▪️Learning or focus difficulties
▪️Mood disturbances
▪️Sleep disruption
▪️Nerve inflammation
▪️Slower reaction times
Lead accumulates slowly, so even low levels consumed repeatedly can be concerning.
Cadmium: A Kidney and Bone Health Concern
Cadmium stays in the body’s tissues for decades.
Long-term risks:
▪️Kidney stress and filtration problems
▪️Calcium depletion
▪️Bone weakness
▪️Hormonal disruption
Higher cacao %, such as 70–90% bars, tend to show higher cadmium levels because they contain more cacao solids.
Arsenic: A Metabolic and Immune Disruptor
Chronic arsenic exposure has been linked to:
▪️Impaired immune response
▪️Metabolic changes leading to fatigue
▪️Cellular oxidative stress
▪️Increased inflammation
Even when present in small amounts, arsenic contributes to the overall toxic load.
Mercury: Neurological Toxicity
Mercury is less common in chocolate but can appear via industrial contamination.
Possible effects:
▪️Reduced motor coordination
▪️Memory lapses
▪️Mood swings
▪️Immune dysregulation
Even small amounts can affect sensitive groups such as pregnant women and children.
Pros and Cons of Chocolate Consumption
Pros
1. Strong antioxidant profile helps slow aging : Cacao’s flavonoids reduce oxidative aging at cellular and skin levels.
2. Promotes heart health : Improves circulation, reduces arterial stiffness, and helps manage blood pressure.
3. Natural mood enhancer : Chocolate triggers neurotransmitter release that improves mood naturally.
4. Cognitive and memory support : Ideal for students, professionals, and anyone seeking sharper mental function.
5. Supports healthy appetite control : Reduces the likelihood of binge eating or dessert overconsumption.
6. Provides essential minerals : Including iron (for energy), magnesium (for relaxation), and copper (for immunity).
Cons
1. Heavy metal contamination in some chocolates : A growing concern among consumers and health experts alike.
2. High calorie density : Overconsumption can lead to weight gain over time.
3. Sugar content in non-dark varieties : Milk chocolates and commercial products can cause blood sugar spikes.
4. Risk of emotional eating : Some individuals may turn chocolate into a coping mechanism, leading to daily overuse.
The good news is that eating chocolate in moderation is unlikely to cause significant health problems for most people. However, being aware of these risks allows you to make smarter choices, such as selecting brands with lower metal levels or enjoying chocolate as an occasional treat. By staying informed, you can keep chocolate delightful and safe!
Choosing Chocolate with Confidence
Feeling the need to part ways with chocolate, your sweet source of solace during life’s low moments? Absolutely not! While concerns about heavy metals like lead and cadmium in chocolate are valid, you can still indulge in moderation with peace of mind by making informed choices.
Pick Trusted Brands: Choose brands that prioritize quality and transparency in their sourcing and production processes. Look for chocolates that are certified organic or fair trade to ensure higher safety and ethical standards.
Mix Up Your Treats: Reduce exposure to heavy metals by alternating chocolate with other snacks like fruits, nuts, or yogurt-based desserts. This variety not only lowers risk but also keeps your snacking exciting.
Moderation is Key: Enjoy chocolate a few times a week instead of daily, especially if you prefer high-cocoa dark varieties.
Pink Tiger Approved Chocolate
Pink Tiger is an initiative that involves independent third-party lab tests to screen for contaminants, including heavy metals like lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic. Products must meet stringent criteria to earn the “Pink Tiger Approved” label, ensuring they are free from harmful substances. If you’re craving chocolate, choose one that upholds the highest standards. Look for the Pink Tiger stamp, a symbol of quality you can trust. Discover our thoughtfully selected range Here 👇🏻

Savour the Sweet
Chocolate is more than just a treat; it’s an emotion, a moment of joy, and a way to care for yourself. Choose brands that test for heavy metals like lead and cadmium, prioritising transparency and safer sourcing. By being mindful of your choices, you can continue to enjoy this beloved indulgence without compromising your health or values.
Indulge Smartly, Protect Confidently
Heavy metals in chocolate shouldn’t scare you away from your favourite indulgence.
They should simply guide you to better brands, better sourcing, and better habits.
▪️Make informed choices.
▪️Support transparent brands.
▪️Choose Pink Tiger Approved products.
▪️Enjoy chocolate the way it was meant to be enjoyed—joyfully and safely.
Your health and happiness deserve nothing less.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is chocolate unsafe now because of heavy metals?
Chocolate isn’t suddenly unsafe; the issue is about awareness, not alarm. Heavy metals occur naturally in soil and can enter cacao through farming or processing. Most chocolates are still safe to consume, especially when eaten in moderation. The key is choosing brands that test their products and maintain transparent sourcing practices, ensuring you’re enjoying your treat without unnecessary exposure.
2. Is dark chocolate riskier than milk chocolate?
Generally, yes, because dark chocolate contains a higher percentage of cacao solids, the part of the plant most likely to absorb heavy metals like cadmium from soil. Milk chocolate is diluted with milk and sugar, reducing the overall cacao content. This doesn’t mean you should avoid dark chocolate; it simply means you should choose brands with proper testing or responsible sourcing from low-cadmium regions.
3. How can I reduce heavy metal exposure from chocolate?
You can lower your risk by choosing chocolates from brands that publish third-party lab results, selecting products sourced from regions with naturally lower cadmium levels, and avoiding extremely cheap chocolates that may cut corners on quality. It also helps to moderate intake and rotate your snacks, so chocolate becomes part of a varied diet rather than a daily habit that increases cumulative exposure.
4. What makes Pink Tiger Approved chocolate safer?
Pink Tiger Approved chocolates go through independent laboratory testing using randomly selected samples, ensuring brands cannot curate “clean” batches for review. These tests screen for lead, cadmium, arsenic, and mercury, along with verifying ingredient purity and clean manufacturing standards. Only chocolates passing strict benchmarks earn the verification stamp, giving consumers a quick, trustworthy signal of safety and quality.
5. How much chocolate is actually safe to eat?
For most healthy adults, moderate intake around 20–30g of dark chocolate a few times a week, is safe and unlikely to lead to heavy metal accumulation. The concern arises only with excessive daily consumption or chocolates with consistently high metal concentrations. Choosing brands that publish lab testing or are Pink Tiger Approved dramatically lowers risk even if you eat chocolate more regularly.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for any questions or concerns regarding your health.
References :
Balali-Mood, M., Naseri, K., Tahergorabi, Z., Khazdair, M. R., & Sadeghi, M. (2021, April 13). Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Frontiers in Pharmacology. Retrieved May 15, 2025, from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8078867/
Chawla, D., & Sondhi, N. (2016, October 25). Attitude and Consumption Patterns of the Indian Chocolate Consumer: An Exploratory Study. Global Business Review, 17(6), 1412–1426. https://doi.org/10.1177/0972150916660408
Colin, Asmaa, Paul, Jeffrey, Eric, Aedín, & flavan-3-ols. (2012). Effects of chocolate, cocoa, and flavan-3-ols on cardiovascular health: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002916523026928
Eva, Martina, & Judita. (2014). Analysis of consumer behavior at chocolate purchase. https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&profile=ehost&scope=site&authtype=crawler&jrnl=13389971&AN=96728066&h=1fgrBRzDkGCmg1dZLDvyeYYiEGTk9DHmxZK5QdtJVr2jvDVyxXxXQzTnNvrGCNroOnCcZKTaJXS4IavTyZ%2Fhnw%3D%3D&crl=c
Hands, J. M., Anderson, M. L., Cooperman, T., Balsky, J. E., & Frame, L. A. (2024, July 10). A Multi-year Heavy Metal Analysis of 72 Dark Chocolate and Cocoa Products in the USA. Frontiers in Nutrition. Retrieved May 17, 2025, from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11321977/
Katz, D. L., Doughty, K., & Ali, A. (2011, April 7). Cocoa and Chocolate in Human Health and Disease. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling. Retrieved May 22, 2025, from http://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4696435/#s035